Synthetic Biology The Next Biotech Revolution
What is Synthetic Biology?
Synthetic biology is a rapidly evolving field that combines engineering principles with biological systems. It’s essentially about designing and building new biological parts, devices, and systems, or redesigning existing natural ones for useful purposes. This goes beyond simply modifying existing organisms; it involves creating entirely new functionalities and organisms, often with unprecedented capabilities. Think of it as biological programming, using the building blocks of life – DNA, RNA, proteins – to create custom-designed biological systems.
Engineering Life: The Tools of the Trade
The power of synthetic biology comes from a suite of powerful tools. CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology allows for precise modification of genomes with remarkable accuracy. DNA synthesis allows scientists to create entirely new genes and sequences from scratch, enabling the construction of artificial genetic circuits. Advanced computational tools are used to design and model these systems, predicting their behavior before they are even built. These tools, combined with sophisticated microscopy and analytical techniques, allow researchers to manipulate and study biological systems with unprecedented precision.
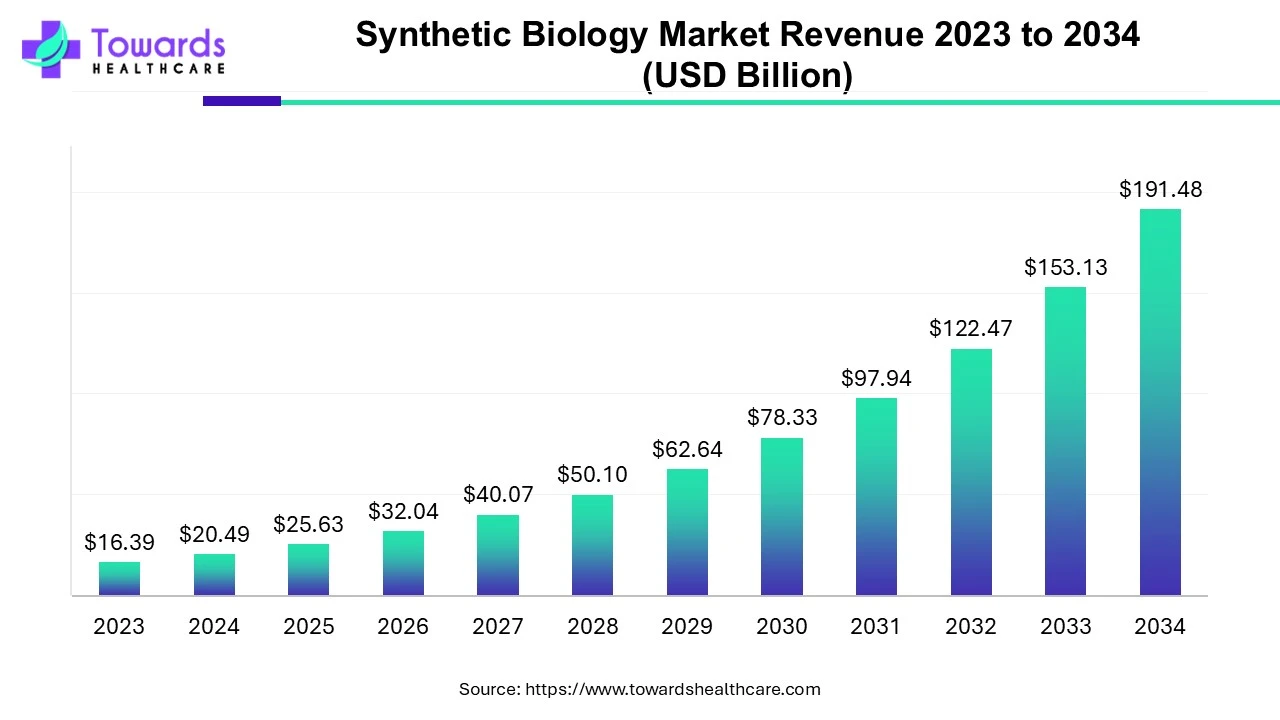
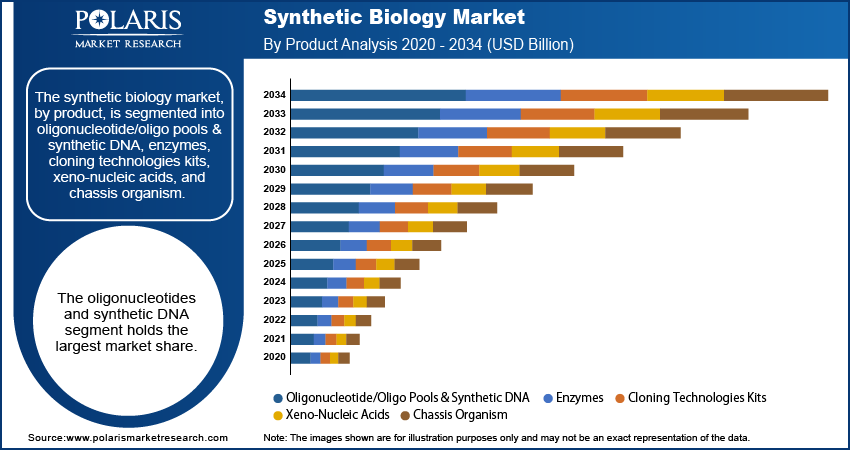
Applications Across Industries: Revolutionizing Various Sectors
The applications of synthetic biology are vast and span numerous industries. In medicine, it holds immense promise for developing novel therapeutics, including new antibiotics to combat drug-resistant bacteria, personalized cancer therapies, and advanced diagnostics. In agriculture, it’s being used to engineer crops with enhanced nutritional value, increased yields, and improved resilience to pests and diseases. In manufacturing, synthetic biology offers sustainable alternatives to traditional chemical processes, producing biofuels, biomaterials, and other valuable chemicals. Even environmental remediation is benefitting, with engineered organisms designed to clean up pollution.
Addressing Global Challenges: Sustainable Solutions
Synthetic biology is uniquely positioned to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges. Climate change, for instance, can be tackled through the development of carbon-capturing organisms and the production of sustainable biofuels. Food security can be improved by engineering crops that are more resilient to climate change and require less water and fertilizer. The scarcity of resources, such as rare earth elements, could be alleviated through the development of organisms that produce these elements in a more sustainable way. These are just a few examples of how synthetic biology offers innovative solutions to global problems.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Innovation
As with any powerful technology, synthetic biology raises important ethical considerations. The potential for misuse, such as creating bioweapons or genetically modified organisms with unintended consequences, must be carefully addressed. Transparency and open communication are crucial to ensure public trust and responsible innovation. Robust regulatory frameworks are needed to guide the development and application of this technology, balancing the potential benefits with the risks involved. Ethical guidelines and public engagement are essential to navigate the complex ethical landscape of synthetic biology.
The Future of Synthetic Biology: A Glimpse into Tomorrow
The field of synthetic biology is still in its relatively early stages, but its potential is enormous. Ongoing research is focusing on developing more sophisticated tools, expanding the range of applications, and addressing the ethical challenges. We can expect to see even