The Rise of the Smart Factory
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Gone are the days of repetitive, manual labor dominating the factory floor. Instead, we’re witnessing the rise of the smart factory, a digitally connected ecosystem where automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence work in harmony to optimize production, improve efficiency, and enhance overall competitiveness. This shift isn’t just a trend; it’s a fundamental restructuring of how goods are manufactured, driven by the need for greater agility, flexibility, and responsiveness in a rapidly changing global market.
Automation: The Backbone of the Smart Factory
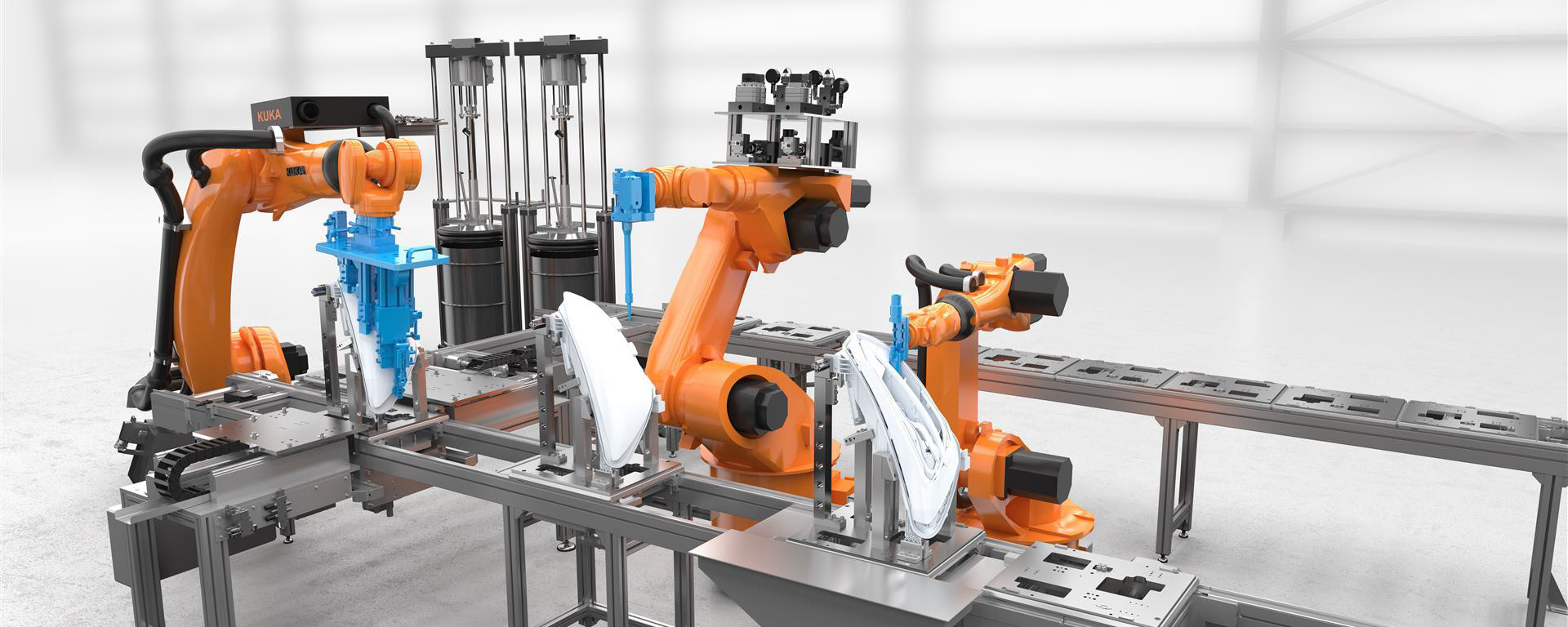
Automation is the very heart of the smart factory. Robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and sophisticated machinery handle repetitive tasks with precision and speed, freeing human workers to focus on more complex and strategic roles. This isn’t about replacing humans entirely; it’s about empowering them to contribute at a higher level. Automation reduces errors, increases output, and ensures consistency in quality, leading to significant cost savings and improved product quality.

The Power of Data Analytics in Manufacturing
Smart factories generate a massive amount of data – from machine performance to energy consumption, production output, and supply chain logistics. The ability to collect, analyze, and interpret this data is crucial. Advanced analytics provide insights into areas for improvement, allowing manufacturers to proactively address potential issues, optimize processes, and predict future needs. This data-driven approach fosters continuous improvement and enhances decision-making across all aspects of the factory operation.
Artificial Intelligence: Enhancing Decision-Making
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly becoming an indispensable tool in smart factories. AI-powered systems can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and anomalies that might go unnoticed by human operators. This enables predictive maintenance, allowing for timely repairs before equipment failures disrupt production. AI can also optimize production schedules, manage inventory more effectively, and even personalize products based on customer demand. The integration of AI is driving a new level of intelligence and autonomy in manufacturing.
The Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting the Factory Floor
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the connective tissue of the smart factory. By linking various machines, sensors, and devices across the factory floor, the IoT creates a seamless flow of information. This allows for real-time monitoring of processes, equipment status, and production performance. The data collected through the IoT forms the basis for the advanced analytics and AI applications that drive efficiency and optimization within the smart factory environment. It truly creates a living, breathing network of interconnected systems.
The Human Element: Collaboration and Upskilling
While automation and AI are crucial components of the smart factory, the human element remains indispensable. The transition to a smart factory requires a workforce that’s equipped with the skills to manage, maintain, and improve these sophisticated systems. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives are vital to ensure that workers have the knowledge and expertise to thrive in this new environment. The focus shifts from manual labor to roles that require problem-solving, critical thinking, and collaboration with intelligent machines.
Supply Chain Integration and Optimization
Smart factories are not isolated entities; they are part of a larger, interconnected supply chain. The ability to integrate and optimize the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to product delivery, is a key benefit of smart factory technology. Real-time data sharing and automated processes across the supply chain enhance visibility, reduce lead times, and improve overall responsiveness to market demands. This end-to-end integration significantly improves efficiency and reduces operational costs.
Security and Cybersecurity in the Smart Factory
With increased connectivity comes the heightened need for robust security measures. Smart factories are vulnerable to cyberattacks that could disrupt operations, compromise data, and even cause physical damage. Implementing strong cybersecurity protocols, including robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption, is essential to protect the integrity and availability of the factory’s digital infrastructure. A comprehensive security strategy is a non-negotiable element of a successful smart factory implementation.
The Future of Manufacturing: A Collaborative Ecosystem
The smart factory isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a fundamental shift in manufacturing philosophy. It’s a collaborative ecosystem where humans and machines work together to achieve greater efficiency, quality, and innovation. As technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even greater levels of automation, intelligence, and connectivity within the smart factory, further transforming the manufacturing landscape and shaping the future of production. Read also about automation and robotics engineering.